SI - Threaded Inserts for Plastic
Threaded inserts are precision machined metal components with engineered external features that secure them into Plastic.
SI® brand inserts employ press-in, moulded-in, or heat/ultrasonic installation methods to provide strong, reusable, permanent threads in plastic.
Key Insert Features
- Knurling provides torque out resistance
- A hex shaped body also provides rotational torque resistance
- Opposing knurls and diamond knurling provide pull-out resistance. The longer the insert, the better the pull-out value
- Undercuts and barbs also improve pull-out resistance
Slots found in cold press inserts collapse upon installation and expand during mating hardware assembly to provide torque out and pull-out resistance

Ultrasonic / Heat Staking Inserts
- Ultrasonic - Frictional heat caused by the vibration melts the plastic surrounding the insert allowing easy insertion. When the vibration ceases, the plastic solidifies, locking the insert permanently in place.
- Heat Staking - Installed by pressing the insert into the mounting hole with a thermal press to melt the plastic surrounding the insert.

Moulded-In
Inserts
- Installed during the moulding process, the inserts are located in the mould cavity by core pins. When the mould opens, the core pins are withdrawn leaving the inserts permanently encapsulated in the plastic section with only the threads exposed.
- Installing the inserts during the moulding process eliminates the need for secondary steps or installation equipment.

Press-In
Inserts
- Installed by simply pressing the inserts into pre-moulded or drilled holes. Installation is accomplished using any standard press at any time during the production process.
- Eliminates the need for moulding-in inserts.
- Eliminates the need for heat or ultrasonic equipment.
SI INSERTS
Thermal Heat Staking Insertion
During this process, the insert is placed into a moulded or predrilled hole
- A heated probe contacts the insert heating it to at or above the melt temperature of the plastic
- Localized melting occurs as the insert is driven into place
- The probe is retracted and the plastic re-solidifies around the insert
Ultrasonic Insertion vs Thermal/Heat Insertion
Ultrasonic Insertion Advantages
- Fast and reliable
- Works well for most thermoplastics
- Uses standard 20kHz welders - easy to source
- Repeatable results
Thermal/Heat Insertion Advantages
- Non-Abrasive compared to ultrasonic insertion
- Provides better plastic flow during installation
- Metal dust is not created
- Multiple inserts can be installed simultaneously
- Better method used for larger inserts
- Inserts can be installed on different levels simultaneously
- Tooling, equipment and maintenance costs are lower
Ultrasonic Insertion Disadvantages
- Insertion is noisy
- More abrasive, risk damage to insert
- Can create metal dust during installation
- Limited to the number of inserts that can be installed at once
Thermal/Heat Insertion Disadvantages
- Slower when installing 1-insert at a time
- Longer cool-down time necessary for the insert
SI Inserts
Moulded-In
Inserts are installed during the injection mould operation.
The insert is placed on a core pin in the injection mould and the plastic is moulded around the insert. Proper pin size is important to retain insert in place.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Mould-in Insert
Advantages
- Excellent holding strength
- Excellent plastic flow around insert
- No secondary assembly
- Multiple inserts can be installed during the moulding cycle
Disadvantages
- Longer cycle times - more costly
- Plastic can get into the threads
- Mould Damage possible if misloaded
- Inserts need to be removed before plastic can be reground if plastic part is defective
- Moulded-in Stress & Possible Sink Marks
SI Inserts
Cold Press Insertion
Press-in Inserts for Plastics
- Install by simply pressing the insert into pre-moulded or drilled holes
- Eliminates the need for heat or ultrasonic equipment
- No melting of the plastic. Holding values may be lower
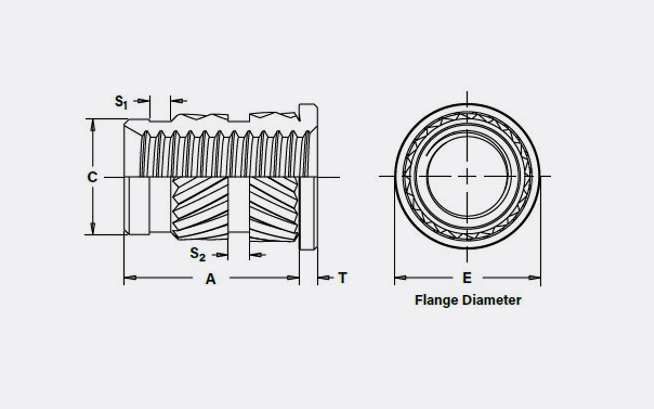
Flanged Threaded Inserts for Ultrasonic and Thermal/Heat Insertion
Flanged, Straight Wall, Thru-Threaded, IUTFB™ Inserts
- Provides larger surface area and high pullout in reverse entry applications
- Brass flange offers a contact surface for electrical connections
- Flange helps distribute the load applied when fastening prior to installation
- Aluminum and stainless steel available upon request
Compression Limiters
Compression limiters are non-threaded inserts that are commonly used in applications where a compressive load is applied to a plastic assembly.
The compression limiter strengthens the plastic and withstands the compressive force that is applied when a mating screw is tightened in the assembly. The integrity of the plastic is not compromised by the load that is applied.